|

Over time, your Hard Disk fills up with all kinds
of stuff, and before you know it, that drive you bought just a year
or so ago, and whose capacity looked great back then, is already
alarmingly full. You need a certain amount of "headroom" or empty
space on your harddrive for Windows to function properly. Things
like the Windows swap file require empty space on the harddrive for
standby utilization and your system can slow down enormously if
it's not available.
- Uninstalling unused components
- Deleting Temp Files
- Deleting other files
- Temporary Internet Files
Uninstalling unused Components
Many people never bother to check which components of Windows
are installed, and which ones can be removed. Are you using
Microsoft Fax Services? If not, you can save around 3.7MB. Use
Internet Explorer, but not MSN Explorer? Uninstalling MSN Explorer
gets you 13.5MB back! Don't play the "standard" Microsoft games?
They use 12.1MB of space!
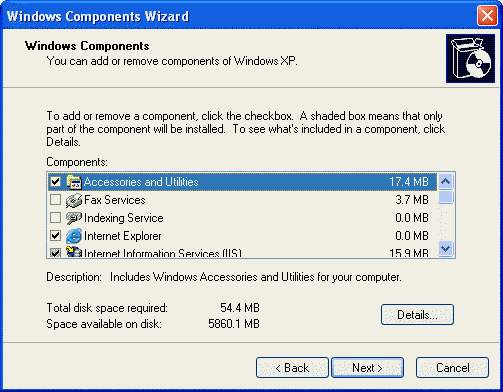
To uninstall Windows components:
- Open your Control Panel (select Start -> Control
Panel)
- Open Add or Remove Programs
- Click the Add/Remove Windows Components button
- Select the components you want to remove and press OK
(see picture 1).
|
| Picture 1
|
Deleting Temp Files
When Windows crashes, or locks up and you have to use
Ctrl+Alt+Del to restart, some temporary files will be left
on your disk. Some installation routines will also leave temporary
files behind.
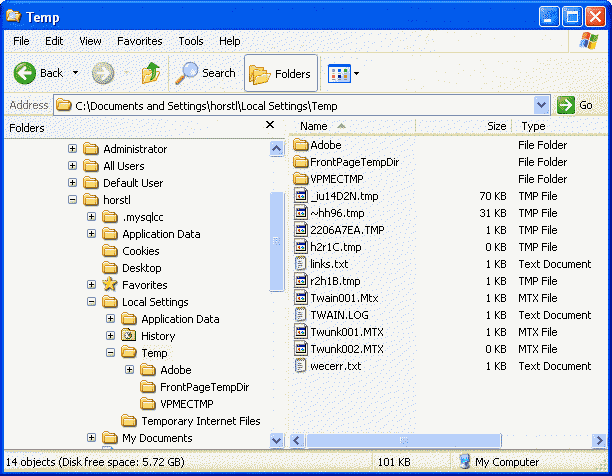
These files will be left in your \Documents and
Settings\your username\Local Settings\Temp folder.
You can use Windows Explorer to find and delete these
files. To be on the safe site, don't delete files with today's
date, these files could still be in use (most probably you'll get
an error telling you that a file can't be deleted because it's in
use) (see picture 2).
|
| Picture 2
|
You can also check your entire hard disk, to see if there are
any temp files in other places:
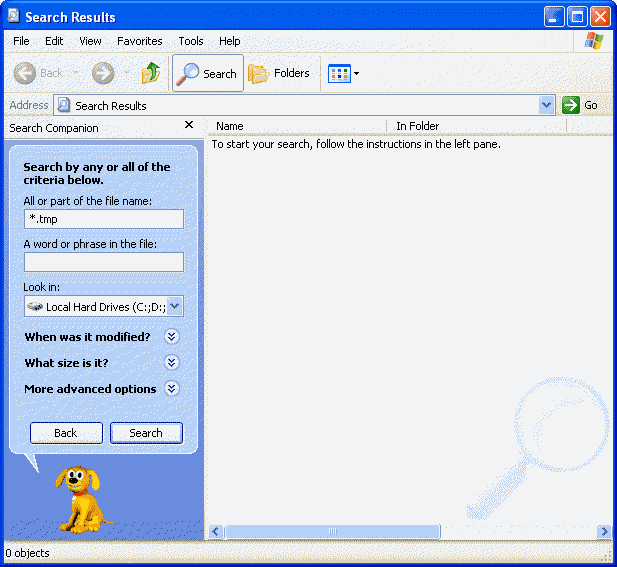
- Open Windows Explorer, and select your drive (e.g.
C:\)
- Press F3, this will open Search
- In the Search for files or folders named: (in box enter)
*.tmp
- Select the drive you want to search in the Look in: box
- Press Search Now (see picture 3)
|
| Picture 3
|
Deleting other files
Other files you could delete are files with these
extensions:
- .dmp - Dump file. When Windows (or an application)
experiences a crash, a memory dump is performed. If you don't use
these files (for trouble shooting), delete them, you can save quite
a bit of space!
- .bak - Backup file; when a new (data) file is created,
some programs will rename the old version with a .bak extension. Be
careful when removing these files.
- .cnt - Help-related file; ever notice those tables of
contents when you launch certain Help files? If you don't need a
table to help you navigate through a Help file, delete these. They
will not come back.
- .fts - Help-related file; when you perform a search with
a Help file, this is created to make all future searches be
performed quicker. E.G., not worth having around unless you use
Help files on a daily basis. They are re-created if you do a search
in a Help file, so these should be regularly scanned for and
deleted.
- .gid - Help-related file; when you run a Help file, it
creates a GID to make future accesses to that particular
help file a tad quicker. They're a complete waste of space. You'll
have to delete these on a regular basis, as they are recreated with
every Help file execution.
- .old - Old file; see .bak.
- .~mp - Temporary file; see .tmp.
- .$$$ - Old file; see .bak (usually, not always)
- .000 - Old file; see .bak
To be on the safe side, delete your files
to the Recycle Bin, and leave them there for a week or two. If you
don't run into any problems, you can empty the Recycle Bin. If
Windows or any program complains about a missing file, just select
your Recycle Bin, find the file and right-click on it. From the
context menu choose Restore. This will restore the file to
its original location.
Temporary Internet Files
Another source of "disappearing" hard disk space are the
Temporary Internet Files. To speed up your Internet browsing,
pages, graphics and other page elements are stored in your
browser's cache. It's worth it to clean this cache from time to
time:
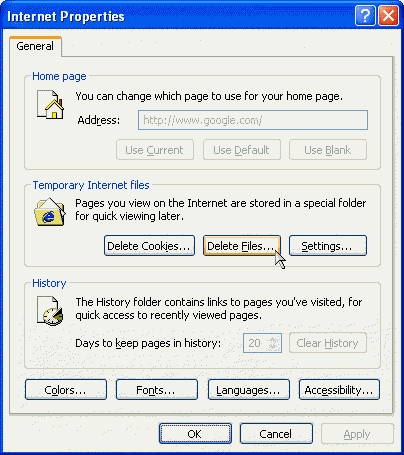
- From the Internet Explorer menu, select Tools ->
Internet Options
- On the General tab, press the Delete Files button
under the Temporary Internet files header
- A Window will pop-up asking you if you want to delete your
Offline content. If you don't download Web sites with
Internet Explorer and view them when you are not connected
(off-line) to the Internet later, you can check the box Delete
all offline content (see picture 4).
|
| Picture 4
|
|





